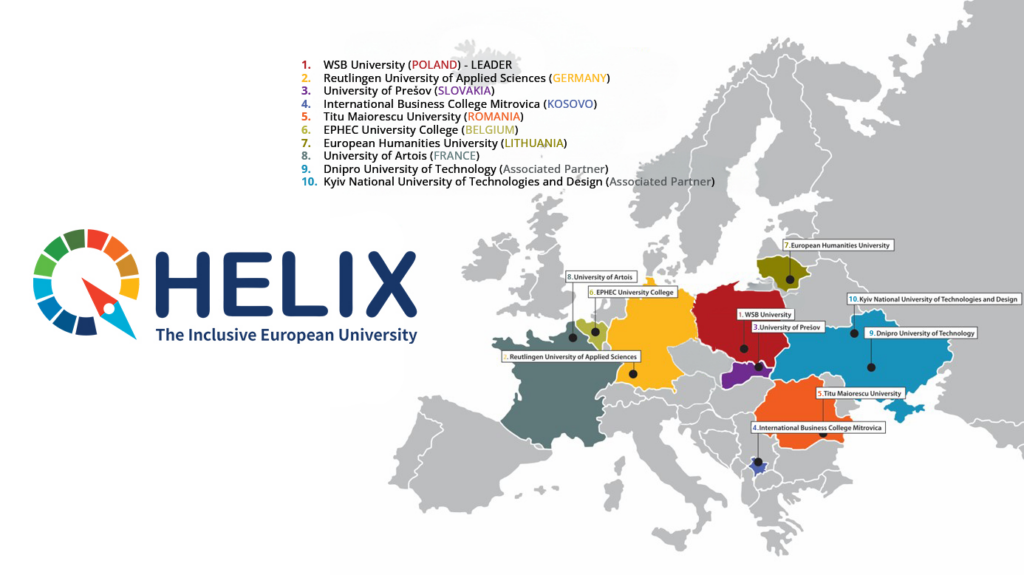
Alliance partners:
- WSB University – Akademia WSB (Poland) – Project Leader
- Reutlingen University of Applied Sciences (Germany)
- University of Prešov (Slovakia)
- International Business College Mitrovica (Kosovo)
- Titu Maiorescu University (Romania)
- EPHEC University College (Belgium)
- European Humanities University (Lithuania)
- Artois University (France)
- Dnipro University of Technology (Ukraine) – Associate Partner
- Kyiv National University of Technologies and Design (Ukraine) – Associate Partner
LIDER: WSB University 
WSB University (AWSB) is a private (non-profit) HEI operated on the Polish market since 1995. According to national rank, WSB is 1st private Polish university outside Warsaw. WSB has 7 branches in South Poland (in Cracow and on Polish-Czech-Slovak border). WSB teaches around 10,000 students from 80 countries on BA, MA and PhD programmes. In the framework of various forms of the non-formal training, it educates 4000 people.
Main disciplines of research, education and activities:
Management and Economics,
Education (Pedagogy),
Security,
Engineering (ICT included),
Health Sciences,
International relations,
Economy,
Medical and paramedical sciences,
Transport and mobility,
Sciences about family.
Main fields of activities:
Social and Educational Innovations,
Sustainable Development,
Security,
Responsible Citizneship.
WSB works in wide international networks of clusters, enterprises, HEIs, research centers, NGOs, local authorities, schools and innovative communities as makerspaces or hubs.
WSB runs:
Social Innovation HUB,
Academic Career Office,
School of Foreign Languages,
Children’s Universities,
Third Age Universities,
Research Institute on Territorial and Inter-Organizational Cooperation,
Centre for Quality and Innovation,
Technology Transfer Center,
Center of Modern Methods and Technologies,
Science Development Department,
The United Nations Club and more.
Target groups of WSB activities are:
Students,
Local communities,
Polish, Czech and Slovak citizens,
People with fewer opportunities,
Seniors,
Children,
Ukrainian Migrants.
At WSB University works 280 paid staff. Since 2013 WSB University and its researchers worked on over 120 projects (funds: around 50 mln euro), under Horizon Europe, Visegrad Fund, Horizon 2020, Erasmus + Strategic Partnerships, Erasmus + Cooperation Partnerships, Erasmus + Knowledge Alliances, The Internal Security Fund – Police (ISFP), Interreg Central Europe, Interreg PL-SK, Interreg CZR-PL, AI for Earth, COST Actions, National EFRD programmes, etc. WSB focuses on interdisciplinary research in international teams with administrative support of Science Development Department. Main fields of research are: Management and Economics, Education, Security, Engineering (ICT included), Health Sciences. WSB works in wide international networks of clusters, euro-regions, enterprises, HEIs, research centers, NGOs, local authorities, schools and innovative communities as makerspaces or hubs. WSB runs Social Innovation HUB, Research Institute on Territorial and Inter-Organizational Cooperation, Centre for Quality and Innovation, Technology Transfer Center and Center of Modern Methods and Technologies.
WSB received following accreditations: CEEMAN (International Quality Accreditation), EUA (European University Association), KAUT (Polish Accreditation Commission of Universities of Technology) on ICT degree programmes. WEB was also awarded with HR Excellence.
Based on partner agreements, the University cooperates with entrepreneurs – members of the following institutions and organizations: Regional Chamber of Commerce in Katowice, Leviatan Confederation (Polish Confederation of Private Employers) and with units of the local administration that shape the region’s innovation policy (Marshal Office of the Silesia Province or Silesian Center of Entrepreneurship).
The University implements other forms of the non-formal education focusing on the increase of the region’s, companies’ and students’ competition on the international labor market:
-WSB Science Academy, Science Festivals, training projects addressed to social groups, School of Leaders, Youth Academy of Media (MAM), E-Teacher Academy.
WSB University is running Social Innovation Hub which supports Polish and European Citizens with fewer opportunities. One of main focus groups are Ukrainian migrants, which received psychological support, but also training and mentorship during employment processes in Poland.
WSB students from Ukraine are interpreters and supports local authorities in inclysion of Ukrainian Migrants. WSB also educates about multidimentional approach to migration on different study circles, ie. National Security, International Relations or Management.
WSB University conducts activities in line with the implementation of 17 Sustainable Development Goals and 169 activities related to them contained in the document “Transforming our world: Agenda for Sustainable Development – 2030”, with particular emphasis on 7 of them, including goal 4 “Good quality of education “, which is a task to provide everyone with sustainable, fair and high-quality education and goal 9 related to supporting Innovation. The proposed project of developing a method, tools and activities for youth workers and teachers contributes to the implementation of these goals. It is worth noting that the WSB University obtained the international Responsible Management Education Partner certificate issued by GPM Global for the years 2022-2023. A team of 18 research, teaching and administrative staff at WSB University participated in Green Project Management (GPM) certification training. This is an international certification, recognized in one of the fastest-growing areas of knowledge and competence of tomorrow – sustainable development. GPM works with many universities around the world, on all continents.
The Green Project Management approach focuses on managing projects in a sustainable way. It provides 8 skills necessary for sustainable project management, including environmental, economic, and social impact analysis of a project, practical implementation of the UN Sustainable Development Goals in projects, Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) reporting system, responsible communication, ethical value chain, people development through projects in an organization, sustainable resource management, closed-loop economics.
Partner: Artois University
General profile of the institution (education – research – service to society)
The University of Artois (henceforth Artois) has a student population of almost 12,500 within its 5 campuses in the Hauts de France region. The campuses are Arras (Human Sciences), Béthune (Applied Sciences), Douai (Law), Lens (Sciences and Tertiary Sector) and Liévin (Sports). Each campus is located in a medium-sized city (between 25,000 and 40,000 inhabitants).
Artois has 500 administrative staff (66% of women) and 609 teaching staff (43% of women).
Since its beginnings in 1992, Artois has established itself as a major contributor to local development, social mobility and professional education. We are a modern and dynamic institution which is in perfect harmony with the educational system, offering innovative teaching and combining the acquisition of knowledge with vocational skills.
A policy of international openness:
Artois has always pursued a policy of international openness. Partnerships (over 250) have been consolidated with various universities and research centers worldwide in the form of bilateral agreements, exchange programs, blended intensive programs double degrees, and cotutelles doctorates.
Artois is a member of EURAXESS France Network, a European initiative that supports the mobility of international researchers. and has also been awarded the « Bienvenue en France » (welcome to France) label by the Ministry of Higher Education.
Experience in (setting up) course management systems for virtual campus (Moodle)
The Moodle LMS was made available to our staff in 2010, with increasing usage over time and a multiplied interest during the health crisis. This year, we have counted 896 teachers who have proposed at least one course. Currently, 4,218 courses are online and concern a little over 10,000 students in total.
Until 2016, we offered annual training workshops at each of the university’s sites. As teachers gradually took ownership of the platform, these workshops were progressively replaced by tutorials, individualized support, or on-demand training, which are more appropriate and appreciated.
At the request of teachers or initiated by educational engineers, various plugins have been installed. Among the most popular are Group choice (group work), Zoom meeting (video conferencing), appointments (making an appointment with a teacher), Wooclap (online quiz), compilatio (anti-plagiarism), and H5P (formatting). Also, note a very strong use of assignments and tests (native plugins in the platform).
Using Moodle, we offer 7 entirely remote degree programs, including several Master 1 and 2 programs. These programs offer approximately 150 courses for a little over 500 students each year.
We set up a web TV in 2014 (https://artoistv.univ-artois.fr), which allows teachers to upload videos for pedagogical or research purposes. It also includes videos from students submitted as part of their studies. To date, almost 3,000 videos are online, with around 1,500 being broadcast privately for Moodle use.
We have recently implemented an automatic subtitling system, currently only available in French.
Finally, the Zoom platform, acquired during the health crisis, remains widely used for colloquiums and research seminars, with the possibility of subtitling in many languages.
The university offers a wide spectrum of courses, both in Initial and Further Education. Courses are well-balanced and in line with the European LMD (Undergraduate, Masters, and Doctoral studies).
BETHUNE INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY (Béthune)
A THREE-YEAR DEGREE
Chemistry
Civil Engineering
Mechanical Engineering and Computer-integrated Manufacturing
UNDERGRADUATE PROFESSIONAL DEGREE (3 YEARS)
Industry Careers: Robotics and Mechatronics
Industry Careers: Mechanics
Construction Careers: Building and Construction
Construction Careers: Public Works
Construction Careers: Civil Engineering and Construction
Construction Careers: Environmental and Energy Performance of Buildings
Health Careers: Food and Nutrition
Analytical Chemistry: Quality Checks and Environmental Assessment
Quality, Hygiene, Health and Safety, Environment
Maintenance and Technology: Pluritechnical Systems
Materials and structures: Management, Design and Production
Industrial Careers: Managing Industrial Production (pending accreditation)
A THREE-YEAR DEGREE
Electrical and I.T. Engineering for Industry
Logistical Industrial Quality and Organisation
Telecommunication Networks
UNDERGRADUATE PROFESSIONAL DEGREE (3 YEARS)
Computing and Information Technology and Telecom Networks Careers
Industry Careers: Managing Industrial Production
FACULTY OF APPLIED SCIENCES (Béthune)
UNDERGRADUATE DEGREE
Engineering
UNDERGRADUATE PROFESSIONAL DEGREE (3 YEARS)
Industrial, Production and Energy Systems Maintenance
Industrial Product Design
Construction Careers: Energy and Environmental Performance of Buildings
MASTER’S DEGREE
Civil Engineering
Electronics, Electrical Energy and Automation
Industrial Engineering
UNDERGRADUATE PROFESSIONAL DEGREE (3 YEARS)
Logistics and Flow Management
MASTER’S DEGREE
Production, Management, Logistics and Purchasing
FACULTY OF SCIENCES (Lens)
UNDERGRADUATE DEGREE
Chemistry
Physics and Chemistry
UNDERGRADUATE PROFESSIONAL DEGREE (3 YEARS)
Food Industry: management, production and product valorisation
Environmental Protection and Management
Landscape Gardening: design, management and maintenance
MASTER’S DEGREE
Chemistry
Nutrition and Food Sciences
UNDERGRADUATE DEGREE
Computing and Information Technology
Mathematics
MASTER’S DEGREE
Computing and Information Technology
Mathematics
LENS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY (LENS)
A THREE-YEAR DEGREE
Computing and Information technology
Multimedia and Internet Carreers
UNDERGRADUATE PROFESSIONAL DEGREE (3 YEARS)
I.T. Carreers: Designing, Developing and Testing Software
Digital Careers: Designing, Editing and Building Websites
A THREE-YEAR DEGREE
Marketing Techniques
Company and Administration Management
UNDERGRADUATE PROFESSIONAL DEGREE (3 YEARS)
Management and Accounting: Managing Client Portfolios in Accounting Films
Marketing Products and Services
Marketing Tourism Products
Commerce and Distribution
Assistant in Human Ressources Management
E-Commerce and Digital Marketing
FACULTY OF ECONOMICS, MANAGEMENT AND SOCIAL SCIENCES (Arras)
UNDERGRADUATE DEGREE
Economics and Management
Social and Economic Administration
MASTER’S DEGREE
Human Resources Management
Marketing and Sales
Entrepreneurship and Project Management
Currencies, Banking, Finance ans Insurance
Sectorial Management
FACULTY OF HISTORY, GEOGRAPHY AND HERITAGE STUDIES (Arras)
UNDERGRADUATE DEGREE
History
Geography and Planning
UNDERGRADUATE PROFESSIONAL DEGREE (3 YEARS)
Landscape Gardening: Design, Management and Maintenance
Training for Tour Guides
MASTER’S DEGREE
Geography
History, Civilisations and Heritage
Religious ans Social Sciences
Territorial Management and Local Development
FACULTY OF FOREIGN LANGUAGES (Arras)
UNDERGRADUATE DEGREE
Foreign and Regional Languages, Literature and Civilisations
Foreign Languages Applied to Business
MASTER’S DEGREE
Foreign and Regional Languages, Literature and Civilisations
Foreign Languages Applied to Business
FACULTY OF LETTERS AND ARTS (Arras)
UNDERGRADUATE DEGREE
Literature
Performing Arts
MASTER’S DEGREE
Performing Arts and Live Shows
Teaching French as a Foreign Language (FLE)
Museum and Expographic Studies
FACULTY OF LAW (Douai)
UNDERGRADUATE DEGREE
Law
UNDERGRADUATE PROFESSIONAL DEGREE (3 YEARS)
Legal Activities
MASTER’S DEGREE
Legal Proceedings
Local Authority Law
Environment and Town Planning Law
Company Law
FACULTY OF SPORTS AND PHYSICAL TRAINING (Liévin)
UNDERGRADUATE DEGREE
Science and Technique of physical ans Sports Activities
MASTER’S DEGREE
Health adapted physical activity
DEUST
Animation, Marketing Sports Provision
Research at Artois and Open Science:
Artois has a bold and demanding research policy. On the strength of its 17 approved Research Units, Artois University fosters and develops research excellence built around 4 Fields of Major
Interest (« DIM » : Domaine d’Interêt Majeur), in connection with national and European scientific projects:
DIM 1: Artificial intelligence
DIM 2: Environmental Energy Efficiency
DIM 3: Heritage, Territories and Cross-Cultural Awareness
DIM 4: Reconfigurating the social fabric : Assessing, Explaining and Taking Action
Below is the list of the research laboratories that are in alignement with Q-Helix:
Centre de Recherche en Informatique de Lens (CRIL): Lens IT Research Centre (UMR CNRS 8188) Lens, Faculty of Sciences and Institute of Technology
Civil Engineering and Geo-environmental Laboratory – LGCgE, Béthune, Faculty of Applied Sciences
Electrotechnical Systems and Environment Laboratory – LSEE, Béthune, Faculty of Applied Sciences
Artois IT Engineering and Automation Laboratory – LGI2A, Béthune, Faculty of Applied Sciences and Institute of Technology
Blood-brain Barrier physiopathological Laboratory – LBHE, Lens, Faculty of Sciences
Catalyst and Solid State Chemistry Unit – UCCS (UMR CNRS 8181) Lens, Faculty of Sciences
BioEcoAgro, Lens, Faculty of Sciences
Multi-disciplinary Research Unit : Sports, Health and Society – URePSSS, Liévin, Faculty of Sports and Physical Education
LEM Laboratory – Artois team (UMR CNRS 9221) Arras, Faculty of Economics, Management, Administration and Social Sciences
RIME Laboratory – Artois team, Arras, Faculty of Economics, Management, Administration and Social Sciences and Lens Institute of Technology
More details on some key areas:
Artificial intelligence
The research at CRIL deals with the design of autonomous intelligent systems.
Depending on the information available, such systems should be able to take reasonable decisions to reach given goals. To do so, some form of reasoning is needed. The main difficulties to be solved to realize such systems are diverse.
First, the information to be exploited must be acquired. It can be learned from various types of data (descriptions of situations or scenarios, examples of use cases, operating traces and so on.) but also transmitted by different sources or agents with which the system under consideration interacts. Taking these sources into account requires the ability to synthesize, aggregate and reformulate the processed information in order to be able to exchange it and transmit the results (decisions, predictions, recommendations, and actions to be taken) to the users (other agents, human or not) in an appropriate form. It is also necessary to be able to make this information evolve and to manage its dynamics, in particular when conflicts appear.
The available information is usually heterogeneous and imperfect. It typically includes knowledge transferred or extracted from data, beliefs about the state of the world in which the intelligent system evolves (e.g: physics law, but also data gathered from more or less reliable sensors). It contains the information about the other agents found in that world, the description of available actions and their effects, the preferences of the agents on the state of the world or the actions to perform. The imperfection of available information has several facets (which are correlated): incompleteness, uncertainty, inconsistency, contextuality, among others. In all cases, it is necessary to define models adapted to these different types of information, but also to design and analyze information representation formalisms that are appropriate to the targeted tasks.
The kind of inference necessary to simulate an “intelligent” behavior are multiple and must be modeled. It is also necessary to be able to explain the reasoning that is carried out, to justify given decisions and to evaluate their robustness. Finally, a last source of difficulty to integrate is linked to the computer: the inference and decision making processes considered are often sophisticated and computationally intractable in the worst case. It is therefore important to identify the sources of complexity involved in order to overcome them as best as possible, by developing efficient algorithms in practice, or by developing methods such as approximation or compilation that can sometimes avoid this computational difficulty.
In order to address these challenges, CRIL organizes its activities along three main and interconnected axes: data, knowledge, and constraints.
Civil Engineering and Geo-Environment
The Laboratory of Civil Engineering and geo-Environment (LGCgE) was created in 2010 with the aim of bringing together regional research potential in the field of geo-materials, civil engineering, building and geo-environment. The main goal is to meet the challenges of exploring new civil engineering materials, deep understanding of soils and environment problems, sustainable construction, the protection of natural resources and the management of industrial sites.
The LGCgE is headed by the Artois University, the University of Lille, IMT-Nord Europe and Junia. Organized into 5 research teams, the laboratory has more than 200 members. In order to reinforce the inter-team cooperation, the laboratory has created two transversal operations respectively on “Materials” and “City”. These operations aim to consolidate existing cooperation and explore new cooperation.
The main activities of LGCgE range from geo-materials (important constituents of infrastructures) to buildings. The whole leads to the city of tomorrow and takes into account the related environmental aspects. These latest emerging topics respond to the problems linked to soil, water and air pollution. Experimental and theoretical means are also available. These two major components are complemented by research on housing and the smart city to form a united whole in a laboratory of civil engineering and geo-environment.
Electrical Engineering
The research conducted at the Laboratory of Electrotechnical Systems and Environment (LSEE) focuses on the environmental efficiency of rotating electrical machines and transformers. In other words, the researchers at the laboratory design more efficient electromagnetic components that are constrained by their applications and accepted in their environment. A good example is an electric actuator embedded in an aircraft: it needs to be lightweight, reliable, and powerful.
Thus, the team works together on two closely related pathways:
1. The design of efficient and silent electrical machines. This efficiency research relies, for example, on the use of high-performance electrical steels and the dimensioning of specific machines by developing original methods.
2. Structural reliability with the detection of aging-related faults or the improvement of Electrical Insulation Systems (EIS). The researchers implement breakthrough materials or develop original models to understand the complex phenomena that occur within the windings.
These two themes converge on the common goal of designing machines capable of withstanding extreme internal temperatures.
A strong and historical identity of LSEE lies in the systematic validation through experimentation. The testing facilities are renowned and contribute to the laboratory’s strong appeal.
Logistics
The LGI2A laboratory (Laboratory of Computer Engineering and Automation of Artois) is a host team of the Ministry of National Education, Higher Education and Research (UR 3926). It currently is composed of more than fifteen research lecturers within a single “Decision support” team. This team revolves around two major scientific themes : Optimization of Complex Systems, Uncertainty management.
Our laboratory’s flagship applications focus on sustainable logistics and mobility.
Applications areas : Smart Mobility, Sustainable logistics, decision and information fusion (DFI theme), OptiSCo theme (methods for solving notoriously difficult and often combinatorial problems encountered in logistics systems).
Biology
Blood-brain barrier (BBB) is localised at the brain microvessel level and isolates the brain from the whole body. This barrier represents an obstacle to deliver drugs into the central nervous system. Therefore there is a real need to better understand this barrier to treat neurodegenerative diseases.
Our laboratory has been investigating BBB for at least 30 years by developping in vitro models using animal but also human cells. With these in vitro models, we study BBB physiology in normal and pathological conditions. We also aim to better understand molecular and cellular mechanisms involved in drugs passage across the BBB in order to improve diagnostic or therapy for neurological diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease, stroke, Parkinson’s disease, etc
Currently, the laboratory is composed of 9 researchers, 8 technical members and students/post-doc. Among our different in vitro models, we developped and patented a human BBB model consisting to cultivate CD34+-derived endothelial cells with brain pericytes. We also develop human models based on iPSCs. The technical platform (SMART platform, with 2 mass spectrometers) allowing us to measure drug/molecule passage across the BBB.
The BBB-Lab was involved in several national and european projects. We have participated in 2 FP7 2008-2013 : EUSTROkE, focusing on stroke, and PREDICT IV, aiming to develop in vitro models to assess drug toxicity. We also were involved in the european project ACUTETOX, for predicting the neurotoxicity of chemicals in the frame of the REACH legislation.
We are currently involved in these following projects : BtRAIN, SNOWBALL, DIASYN, In3, NanoStem, CNS Antidote, MAGBBRIS & NINTARMAL.
Agro-food
The Transborder Joint Research Unit BioEcoAgro is a new structure created in January 2020, bringing together approximately 300 researchers and technicians from both sides of the Franco-Belgian border, including those from the regional biotechnology and agri-food research laboratory, the Charles Viollette Institute, on the French side. Its ambition is to develop an international center of excellence in the field of applied biological engineering for agriculture, biotechnology, agri-food, and the environment.
This research unit is divided into 3 main thematic areas, each comprising 3 research teams. The “Structure-Function Relationship for Rational Formulation of Ingredients and Food” (FRAI) team belongs to Theme 3, “Formulation – Food Quality and Safety – Nutrition – Health.”
This multi-site team brings together researchers from the University of Artois, the University of Littoral Côte d’Opale, JUNIA-ISA Lille, and the University of Liège (Gembloux AgroBioTech). The team based in Arras consists of about ten individuals, including 3 professors, 2 assistant professors, a research engineer, a secretary, and doctoral students who are hosted at the ADRIANOR agri-food technical center located in the ZI Est in Tilloy-les-Mofflaines.
Our approach, implemented in Arras, Boulogne-sur-Mer, and Lille, consists of considering the entire life cycle of a food product, from the raw materials used in its production to its consumption. This approach combines scientific expertise in fundamental research (such as determining the secondary and tertiary structure of proteins) with applied research (such as sensory evaluation of products) to analyze and investigate the various physicochemical mechanisms governing the evolution of the organoleptic, textural, and nutritional qualities of food. Therefore, our research activities revolve around three axes, which, through an integrated and rational approach, enable the development of high-value-added food products.
Axis 1: Variability of raw materials and their sources
Axis 2: Techno-functional ingredients: structure-function relationship
Axis 3: Impact of formulation, manufacturing processes, and storage conditions on food quality
The applied research conducted within these three axes allows us to meet the needs of agri-food industry professionals with whom we collaborate at both the regional and national, and even international levels. Likewise, through these axes, the FRAI team is involved in several regional, national, and international research projects, some with a more fundamental aspect.
Sports and Physical Activities
The approach adopted by the SHERPAS Lab since its foundation in 2002 promotes dialogue between disciplines of socio-logy, history, psychology and physiology, and respect for eachother’s academic practices. These scientific approaches shape the identity of the SHERPAS Lab and place it at the intersection of science and technology of physical sports activities and social sciences. For a quarter of a century, the lab has been committed to studying sports as a scientific topic as well as a social construct. In 2018 a new scientific program was launched, with the goal to interpret the use of the body in the context of physical and sports activities (PSA) and of physical and sports education (PSE), within the framework of the reconstruction and disintegration of social belonging. Our studies aim to examine whether PSA and PSE affect the construction or the consistency of the recognition and protection of the personal and social identities and if so, to what extent. We study these relationships from the opposite perspective: we also seek to know how the isolation of individuals, the threatened cohesion of society, and the decline of institutions can influencethe APS and the EPS. During our research carried out in various contexts and fields, the focus shifted to situations where physical, social, economic, psychological vulnerabilities are detectable. Through adopting multidisciplinary scientific approaches, the conscious use of materials and measures, and being aware of the limitations of these research tools, the lab members carry out high quality research of vulnerabilities. This program is completely in line with the third strategic pillar of Artois University.
Applied Economics
The LEM (Laboratory of Economics and Management) is a Joint Research Unit (No. 9221) that brings together the CNRS, the University of Lille, and the IESEG School of Management, with partner institutions being the University of Artois and the University of Littoral-Côte d’Opale.
The research conducted within the LEM is inherently multidisciplinary. It encompasses both theoretical and applied aspects, and the members of the LEM address requests from economic and social environments. The research conducted at the LEM often addresses important societal issues, as evidenced by our collaborations with the National Research Agency (ANR), the National Cancer Institute (INCA), the Court of Auditors, the European Metropolis of Lille (MEL), among other partners.
the LEM is a young and dynamic laboratory with a strong scientific ambition and a marked international vocation. The quality of the work carried out by LEM researchers has been recognized, with the unit receiving an evaluation by HCERES designating it as “one of the top units in economics and management in France,” and its scientific output being noted as “excellent”.
Artois advocates open access to research and scientific knowledge. This involves sharing research findings, data, methodologies, and other research outputs with the broader scientific community and society at large. This allows researchers, students, policymakers, and the public to access, use, and build upon scientific knowledge, leading to increased visibility, impact, and potential for societal benefits.
Aligned with the current national and European political landscape, Artois has taken a proactive approach in implementing an institutional policy that embraces Open Science. As a result, a dedicated steering committee for Open Science was established in 2022. Aware of its responsibility, Artois is fully committed to the Open Science movement and wishes to support the entire scientific community and users in this process.
Service to society:
There are many ways in which Artois contributes positively to the broader community. Our ambition is to to apply the expertise and resources of the university to address social, economic, cultural, and environmental issues, and to make a positive impact on the well-being and development of society as a whole. Below are a few examples to illustrate our dedication to serving society. (Other actions will be mentioned later in this questionnaire)
Artois and Vivalley Campus
Artois, a partner of Vivalley Campus led by the Lens-Liévin Agglomeration Community and located at the heart of the sports excellence hub in Liévin, the Vivalley Campus positions the Faculty of Sports and Physical Education of Liévin at the core of its ecosystem. Vivalley Campus is a competitiveness cluster in the field of sports, health, and well-being. It brings together businesses, higher education institutions, and research organizations on the same territory, with the aim of working synergistically to implement projects for economic development through innovation. The training programs offered by the Faculty of Sports and Physical Education of Liévin, focused mainly on education, motor skills, sports training, and adapted physical activities for health, attract more than a thousand students. Throughout their academic journey, ranging from Bachelor’s to Doctoral level, students acquire solid knowledge and skills in teaching physical activities to various audiences, as well as in project engineering and design.
The connections established with the companies at Vivalley Campus provide students with opportunities for internships and apprenticeships. Conversely, this partnership offers short-term training programs tailored to the needs of Vivalley Campus companies and professionals. It can also lead to research contracts with the faculty’s researchers who are members of the “SHERPAS” laboratory. This laboratory conducts research in sociological, psychological, physiological, and historical aspects of physical and sports activities. Applied research contracts or action research projects are carried out to address various social demands from the business, non-profit, and public sectors, focusing on health, integration, inclusion, and motor performance.
Life-long learning
Each year, the Continuing Education Service of the University of Artois (FCU Artois) trains over 2000 adult learners, including apprentices, employees on training leave, active employees in companies, job seekers, and individuals under judicial supervision (prisoners).
The close relationships maintained with local, regional, and national economic actors allow Artois to establish cooperative agreements in the field of continuing education to meet the skills demands of companies. For example, the IUT of Béthune established an on-site training program at Air France five years ago for employees of the airline in the networks and telecommunications domain. More recently, there has been a training program in Agroproduction Chemistry with Roquette Frères.
Finally, as part of the institution’s contribution to economic and social development, FCU implements university diplomas (DU), often initiated by economic or institutional partners. In recent years, several diplomas have been established, including a DU in Chinese language and culture in collaboration with the Regional Council of HDF, ethics of AI, a DU in Agroproduction Chemistry, and a DU in Medical-Social Assistant Secretary, which validates the professional title of medical secretary.
European Humanities University
The European Humanities University (EHU) is a distinctive institution that originally started in Minsk, Belarus, in 1992. It was founded to foster critical thinking, openness, and personal responsibility among its students, with the goal of educating a new generation of young professionals capable of leading Belarus toward democracy. EHU was the first private undergraduate and postgraduate university in Belarus. However, due to political pressure, the university was forced to close its operations in Belarus in 2004 and subsequently reestablished itself in Lithuania with support from the Lithuanian government, the European Commission, the Nordic Council of Ministers, and various European countries and international foundations.
Since relocating to Vilnius, Lithuania, EHU has operated as a private Lithuanian university, with its campus located in the UNESCO World Heritage-listed Vilnius Old Town, in the premises of a former late 18th-century Augustinian monastery. The university offers a liberal arts education and is fully integrated into the vibrant life of the Lithuanian capital. EHU provides undergraduate, graduate, and PhD programs in the fields of humanities, social sciences, and arts, with most programs being instructed in Russian and English. The university emphasizes a transdisciplinary approach and critical thinking skills that enable students to develop innovative solutions, ideas, and enterprises.
EHU is committed to academic freedom and serves as a haven for students and scholars from Belarus, being the only Belarusian university that operates in a free and democratic environment. The institution is involved in the Bologna process and ensures that its degrees are recognized within the European Union. EHU also participates in various mobility programs like Erasmus+ and Campus Europae, allowing students to experience education and life across Europe.
Notable is EHU’s support for civic engagement and the development of innovative solutions through hands-on learning opportunities. Students at EHU engage in practical experiences such as participating in the Election Observation: Theory and Practice program, practicing legal skills in moot court competitions and developing projects of their own. This hands-on approach is complemented by the university’s commitment to fostering international and interdisciplinary research and teaching through its faculty who are leaders in academic projects.
Partner: International Business College Mitrovica
IBCM is higher education institution, that offers four BA inter-disciplinary study programmes:
Public Administration and Social Welfare
International Sales and Marketing
Environmental and Agricultural Management
Applied Information Technology
And an MA programme:
MSc in International Management and Leadership, with specializations in:
Environmental Management
Business Management
IBCM’s pedagogical model was developed through a consortium of Danish partners, including the Lillebaelt Academy of Professional Higher Education (EAL), as well as the University College Lillebaelt (UCL) and Tietgen Business College. The partnership is maintained to this day through a double diploma agreement between IBCM, EAL and UCL.
It is at present the only inter-ethnic higher educational institution in Kosovo and one of the most successful international and local efforts to include all communities. It was formed with the aim of improving employability through study programmes with a heavy focus on practice and skills, supporting economic development in the region and bridging the ethnic groups in Mitrovica.
Educational Methodology: From Theory to Practice
The “From Theory to Practice” educational model employed by the IBC-M college is a comprehensive approach that guides students through a learning journey, starting from the Conceptualisation phase, where explicit knowledge is processed through theoretical learning. This phase lays a solid foundation of understanding, providing students with the necessary information and frameworks.
Following this, students transition into the Experimentation phase, where the conceptual knowledge they’ve acquired becomes grounded. This is a critical step as it allows students to apply their theoretical understanding in controlled settings, helping to bridge the gap between theory and practice.
Next is the Experience phase, which provides students with the opportunity to put their tacit knowledge to the test in real-world scenarios. This practical application not only reinforces the tacit knowledge gained from experimentation but also enhances their skills and confidence in their abilities.
In the end, the Reflection phase allows students to bring their inherent tacit knowledge to the surface, encouraging them to think critically about their experiences, draw connections, and internalise the learning. This holistic approach ensures that students are not just passively receiving information but are actively engaged in their learning journey, translating theoretical knowledge into practical skills.
Partner: Reutlingen University of Applied Sciences
Reutlingen University is one of Germany’s leading universities of applied sciences, offering international academic programmes with close ties to industry and commerce. The university campus incorporates five different Schools: Engineering, ESB Business School, Informatics, Life Sciences and Texoversum – School of Textiles.
Reutlingen University offers 46 degree programmes at Bachelor’s and Master’s level, in which we train top executives of the future both in professional and personal development ensuring that they become specialists and managers for whom social responsibility is second nature. Reutlingen University has been consecutively ranked for several years among the top performing educational institutions in Germany, reflecting the high standards of our programmes and the top-class academic education we provide. All our degree programmes are accredited with internationally respected agencies. Since June 2022, the state of Baden-Wurttemberg officially declared its universities of applied sciences to confer doctorate degrees opening a new path for students to further pursue research and further qualification.
Cooperation with the business world, close contacts to industry, and joint teaching and research infrastructures and networks all ensure that we offer the best possible combination of theory and practice. Our research themes stretch over several interdisciplinary fields impacting on global societal challenges e.g. wellbeing, sustainable energy and digital transformation inline also with the UN Development Goals.
What is more, Reutlingen University wishes to promote the principle of life-long learning. The “Knowledge Foundation” offers professional people the chance to attend high-calibre continuing education courses.
Our mission covers four main areas:
Strengthening business by turning out top executives and specialists – for both the German and the international labour market
Strengthening business via applied research, innovation transfer and consulting
Reinforcement of social development by stimulating innovative start-ups and addressing future-oriented issues
Further development of Reutlingen University as an attractive employer
Partner: The University of Presov in Presov, Slovakia
The University of Presov ranks among the most reputable and distinguished universities in the Slovak Republic. The university was officially established by the Act no. 361/1996 Coll. on 1 January 1997 as a division of Pavol Jozef Safarik University in Kosice. This historical event completed the effort of Presov to create its own university having lasted for several years. In the course of its existence, UNIPO has developed into a modern and dynamic university with teaching and research departments. It is a member of Danube Rectors Conference, the European Universities Association and the National Rectors Conferences. The University of Presov is also a co-founder of the Alliance of the Central-Eastern European Universities and Euro-Mediterranean University. The research focus of the university is in the fields of social sciences, natural sciences, theological sciences, physical education and sports, management, arts and health.
The university consists of 8 faculties ((Faculty of Arts, Greek-Catholic Theological Faculty, Faculty of Humanities and Natural Sciences, Faculty of Management, Faculty of Education, Faculty of Orthodox Theology, Faculty of Sports, and Faculty of Health Care) which offer a number of accredited study programmes in all 3 degrees (Bachelor, Master and Doctoral degree) and in both full-time and part-time forms. The University of Presov develops an intense research activity, and it has three centres of excellence, participation in the Competence Centre and the Science Park. A wide range of courses and educational activities are offered by The Centre of Competences and Lifelong Learning.
Partner: Universitatea Titu Maiorescu
Titu Maiorescu University (UTM), established in 1990, is a prestigious private non-profit higher education institution located in Bucharest, Romania, with a branch campus in Târgu Jiu. Recognized by the Romanian Ministry of Education and Research, UTM is part of the National Education System and offers a wide range of academic programs across multiple disciplines.
Academic Structure:
TMU comprises nine faculties:
Faculty of Psychology
Faculty of Law (Bucharest and Târgu Jiu)
Faculty of Medicine
Faculty of Dental Medicine
Faculty of Pharmacy
Faculty of Social, Political, and Human Sciences
Faculty of Economic Sciences (Bucharest and Târgu Jiu)
Faculty of Computer Science
Faculty of Communication
The university provides education at all levels – Bachelor’s, Master’s, and Doctoral degrees – offering 19 undergraduate programs, 25 Master’s programs, and two doctoral schools specializing in Law and Dental Medicine.
Research and Innovation:
UTM is committed to advancing scientific research through its modern facilities and international collaborations. It hosts two doctoral schools across 12 scientific fields and actively participates in European research initiatives such as Erasmus+ and Erasmus Mundus. UTM’s research centers include the Nicolae Cajal Medical Research Institute and partnerships with institutions like Università degli Studi di Roma “La Sapienza” and Technische Universität Dresden.
International Collaboration:
Internationalization is a cornerstone of UTM’s strategy, aligning with the Bologna Declaration to create a common European Higher Education Area. UTM is a member of the European Association of Universities (EUA), International Association of Universities (IAU), and Agence Universitaire de la Francophonie (AUF). The university collaborates with numerous international institutions to promote student and faculty mobility, joint degree programs, and global research initiatives.
Lifelong Learning:
UTM supports lifelong learning through flexible study options, including full-time and distance learning programs tailored to meet labor market demands.
Facilities:
The university boasts state-of-the-art infrastructure, including modern lecture halls, laboratories equipped with cutting-edge technology, student accommodations, medical centers, and recreational facilities. With its strong academic foundation, dedication to research excellence, and focus on international collaboration, Titu Maiorescu University plays a vital role in shaping future professionals while contributing to the goals of the Q-Helix alliance.

EPHEC is an agile institution, capable of continually adapting to changes in its internal and external environment in order to achieve its mission. In this environment, each individual can acquire the training that corresponds to his or her life path, thanks to innovative, participative and caring teaching methods. EPHEC’s mission is to be a committed learning community, where students, teachers and local and international players create innovative learning experiences to reveal everyone’s potential, throughout their lives.
CAMPUSES
EPHEC is currently located on six different campuses, five in the heart of the European capital (Woluwe, Galileo, Schuman-Europe, Lambermont and Delta) and one in the centre of the student town of Louvain-la-Neuve. All our buildings fit harmoniously in urban centres, and are easily accessible by public transport.
All EPHEC buildings have been well-designed in order to encourage exchangs and interaction between the students and stimulate the learning process: Auditoriums of varying sizes, lecture theatres, libraries, computer rooms, learning centre labs, mezzanines, cafeteria…
EPHEC exchange students following programmes in English are welcomed on our main campus of Woluwe. This campus is located 20 minutes by metro from the historical center of Brussels.
Quality Assurance
Policy
Quality at EPHEC is seen as the added value of the skills developed by graduate students over and above the skills they had when registering at EPHEC. It is also reflected in the student’s contributions in terms of social responsibility. The internal quality management system is organised in line with EPHEC’s strategic plan, through a procedure for defining, evaluating and implementing annual objectives. Quality thus flows directly from the strategic plan, and its results feed into it. Our quality management system aims to develop a robust quality culture. The desire for continuous improvement is omnipresent in the practices of our community, at all levels, reflecting a shared vision of the quality culture. The involvement of external stakeholders is frequently sought, motivated by a strong desire to meet the needs of the professional world while working to ensure the long-term employability of our students.
Implementation
The actions that the EPHEC puts in place to ensure quality include :
- Regular evaluations of teaching by students;
- Follow-up evaluations of graduates 1 and 5 years after graduation to gather data on their integration into the working firel and their opinion on the relevance of their studies to their professional lives;
- Advisory councils bringing together professionals from the sectors targeted by the various degrees;
- Biennial professional development interviews for members of faculty and staff;
- Regular satisfaction, motivation and commitment surveys among staff and students.
Stakeholders
“All players, all beneficiaries”: this philosophy, which defines quality management at EPHEC, reflects the desire to see quality as an institutional concern in which all parties are involved. We make sure to:
- contribute to the continuous improvement of the quality of teaching and learning;
- respond to requests from AEQES and provide methodological support;
- design and implement the methodology for evaluating autonomously the quality of the programmes;
- support the visibility and traceability of the continuous improvement actions carried out within EPHEC;
- provide methodological support and documentation for the executive board in establishing its vision, strategy and continuous improvement.
Sustainability
Sustainable development is development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs (Brundtland Report).
EPHEC is convinced that by integrating the values of corporate responsibility and sustainability in its teaching, research and governance, it will open doors for a more inclusive and sustainable tomorrow.
To this end, EPHEC is committed to the United Nations Global Sustainable Goals and all bachelor degrees include courses and practical cases encouraging students to reflect on and contribute to solutions for local and / or global problems.
Moreover, a dedicated committee (composed of students, teachers and staff members) was brought to life in 2020, as well as the position of ‘Sustainable Development Coordinator’ in our staff.
Finally, various projects have been integrated in our bachelor degrees.
Global Sustainable Management Programme: a full semester taught in English (30 ECTS), welcoming students from Business, Finance and Law degrees, in which students will have a theoretical input enabling them to formulate recommendations to a European company that strives to become more sustainable.
In the Bachelor in Accounting, students take part in a workshop on how to make a given company’s model of a given company more circular using the collective intelligence tool offered by CIRCULAB
The Makers Week on our campus of Louvain-la-Neuve is an opportunity for our Marketing, Information Technology and Electromechanics students to use their creativity and technical skills to help people with reduced mobility.
The Bachelor’s degree in Tourism and Leisure Management includes a course dedicated to sustainable tourism in which students address climate change and analyse the sustainability of a tourism offering.
The Green IT seminar where our students learn about the impact of technology on our environment, with their integration project having to meet at least one of the UN’s sustainable development goals.
Kyiv National University of Technologies and Design
Kyiv National University of Technologies and Design (KNUTD) is a state multidisciplinary higher educational institution established in 1930 and located in Ukraine. With its rich history, KNUTD has become a key player in providing higher education in diverse fields such as engineering, fashion and design, light industry manufacturing processes, business, economics, law, chemistry, and more. The University’s mission is centered around delivering top-tier education while fostering research, entrepreneurship, and innovation.
KNUTD administers a comprehensive educational structure, which includes 3 colleges, 5 faculties, 5 institutes, and several research centers. This structure helps provide qualified education at multiple levels, from junior bachelor’s programs to doctorate degrees, supported by a strong emphasis on applied research. Additionally, KNUTD operates 30 research laboratories, including the Educational and Scientific Laboratory of Sustainable Development, which plays a pivotal role in promoting sustainable practices in education and research, alongside KNUTD’s full commitment to the “Leadership of Sustainable Development.”
The University educates approximately 10,000 students each year, including more than 1,826 international students from various countries. In the current academic year (2024/2025), 787 students were enrolled in the colleges, and 1,265 became first-year bachelor students.
The academic staff at KNUTD comprises 450 highly qualified professionals, many of whom are recognized for their leadership in both research and teaching. Their work impacts global academic and research communities significantly.
KNUTD’s educational approach integrates the close relationship “university-business-government” model, ensuring that its programs are aligned with real-world demands and industry needs. For example, the University’s Department of Entrepreneurship and Business runs programs that include specializations such as “Entrepreneurship and Customs-Logistics Activities,” providing students with the skills necessary for modern industries. This entrepreneurial focus is further supported by KNUTD’s research labs, which facilitate innovation, particularly in areas like sustainability and logistics.
Sustainability is a core value at KNUTD, reflected in its operational practices. The university implements constant monitoring and management systems for energy and water consumption, promoting responsible resource use. These practices are part of KNUTD’s broader efforts to embed sustainability into both its educational programs and campus operations, making it an ideal environment for projects focused on youth development and environmental sustainability.
KNUTD’s long-standing commitment to quality education, innovation, and international collaboration, combined with its strong academic staff, extensive student body, and cutting-edge research facilities, positions it as a strong partner for international projects that aim to foster youth skills, creativity, and sustainable development.
Partner: Dnipro University of Technology

University short description
Dnipro University of Technology (hereinafter DniproTech) is the oldest institution of higher education in Dnipropetrovs’k region. Founded at the end of 19th century, the University has grown to an enrolment of more than 13 000 students. The academic process is provided by more than 600 teachers including over 100 professors and 350 associate professors. DniproTech prepares highly skilled professionals for 31 fields of technical and humanitarian studies, including all mining and exploration specialties, fuel, energy and mineral processing, industrial and civil engineering, mechanical engineering, automation systems engineering, computer sciences, economics, law, philology and social work, management etc. Educational and scientific process is provided by 48 departments united into 10 faculties of full-time education, post-graduate and doctoral courses, scientific and research units, Interdisciplinary Institute of Lifelong Learning, 15 cultural and linguistic centers and other units.
DniproTech is a member of international educational and scientific organizations and networks (EUA, BSUN, EAGE, IUR, IGIP, SEFI, WMC, WFURS and others. University is actively participating in EU program: Erasmus+ program activities, Horizon 2020 and other. In 2022 University was a member of 9 international scientific and 21 educational projects, 43 international programs, 107 grants were received by university students, scientists and staff. Strong international cooperation in education and research are established with universities of Germany, Poland, Austria, Lithuania, Hungary, Croatia, Spain, Italy, France, China, Kazakhstan, Armenia, China and other countries.
University has a strong cooperation network with leading regional state and private enterprises, which provides platform for joint practical study and research projects for students and staff. Dual Training Programs with these companies are established for Bachelors and Masters successfully supporting the principle of Knowledge Triangle Integration (Higher education-Research-Business).
DniproTech has seven international cultural and educational centers that collaborate with the European Union and other countries. Teachers in the DniproTech use international experience in the implementation of non-formal educations methods with higher education.
One of key points of the EU integration in educational sphere is reorganization of the learning process. According to the statement “Development strategy of Dnipro University of Technology till 2026” the improvement of the teaching level and development of current and relevant education are the key tasks for it. By the document the formation of university study model should be provided on the basis of combination education, science and innovation, ensuring integration into the international scientific and educational space.
In terms of supporting dialogue between representatives of education at different levels, as well as to promote innovation in teaching and research, DniproTech is working with high school students, advanced training of teachers of schools, colleges, vocational schools and other educational institutions.
Bilateral relations
DniproTech University, located in the vibrant city of Dnipro, Ukraine, is a dynamic and globally-oriented institution with a strong commitment to providing high-quality education and fostering international collaborations. One notable feature of Dnipro University of Technology is offering of 9 Double/Joint Degree Diploma programs in collaboration with partner institutions from around the world. These programs allow students to earn dual degrees or diplomas, enhancing their academic experience and promoting a deeper understanding of international perspectives.
Dnipro University of Technology is an active member of various international educational and scientific organizations and networks. These include the European University Association (EUA), the Black Sea Universities Network (BSUN), the European Association of Geoscientists and Engineers (EAGE), the International Union of Railways (IUR), the International Society for Engineering Education (IGIP), the European Society for Engineering Education (SEFI), and many more. This extensive network of affiliations underscores the university’s commitment to global cooperation and knowledge exchange.
In addition to its memberships in various international organizations, Dnipro University of Technology is deeply engaged in grant programs. The university actively participates in initiatives such as Erasmus+ (including International Credit Mobility of Students and Staff, Capacity Building in Higher Education, and Capacity Building in the Field of Youth), EIT Raw Materials, Horizon 2020, DAAD (the German Academic Exchange Service), OEAD (the Austrian Agency for International Cooperation in Education and Research), and projects funded by the U.S. Embassy in Ukraine and the Black Sea Trust Fund, among others. These grant programs provide opportunities for students and staff to engage in research, mobility, and capacity-building projects, further enhancing the institution’s global footprint.
Dnipro University of Technology has established strong international cooperation in education and research with universities in various countries, including Germany, Poland, Austria, Lithuania, Hungary, Croatia, Spain, Italy, Turkey, France, China, Finland, Kazakhstan, and numerous others. These collaborations facilitate academic exchange, joint research projects, and faculty and student mobility, enriching the overall educational experience.
Furthermore, the university has developed a robust cooperation network with leading regional state and private enterprises. This partnership serves as a platform for collaborative practical study and research projects for students and staff. Dual Training Programs with these companies are a testament to the university’s dedication to supporting the Knowledge Triangle Integration, which emphasizes the seamless interplay between higher education, research, and the business sector. These initiatives provide students with valuable real-world experience and help them bridge the gap between academic theory and practical application.
In conclusion, Dnipro University of Technology stands as an institution deeply rooted in internationalism and a commitment to excellence in education and research. Its extensive network of partnerships, active participation in grant programs, and dedication to the Knowledge Triangle Integration principle demonstrate its unwavering focus on providing a holistic, globally-informed education to its students.
Acting study programs
History and archaeology
Philosophy
Culturology
Philology
Economy
Politology
Journalism
Accounting and taxation
Finance, banking, insurance and stock market
Management
Marketing
Entrepreneurship and trade
Law
Biology
Ecology
Geology
Physics and astronomy
Mathematical modeling of systems and processes
Software engineering
Computer Science
Computer Engineering
System analysis
Cyber security and information protection
Information systems and technologies
Applied mechanics
Materials science
Industrial engineering
Electric power engineering, electrical engineering and electromechanics
Chemical technologies and engineering
Biomedical engineering
Electronic communications and radio engineering
Automation, computer-integrated technologies and robotics
Information and measurement technologies
Environmental protection technologies
Mining
Oil and gas engineering and technologies
Construction and civil engineering
Geodesy and land management
Hydrotechnical construction, water engineering and water technologies
Social work
Tourism and recreation
Civil security
Automobile transport
Transport technologies
Public management and administration
International relations, public communications and regional studies
International Economic Relations
